Posted: November 7th, 2025
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide for Students-2025
Every form of communication — whether a speech, article, advertisement, or social media post — aims to persuade, inform, or inspire its audience. A rhetorical analysis essay explores how an author or speaker accomplishes that goal. It examines the language, tone, structure, and persuasive techniques used to shape meaning and influence readers or listeners.
Although writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem challenging at first, it becomes much easier once you understand the key elements of rhetoric: ethos (credibility), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logical reasoning). These three components form the foundation of any effective argument and help you evaluate how successfully a writer conveys their message.
By mastering these principles, you can analyze speeches, essays, or even advertisements with greater insight. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to crafting a compelling rhetorical analysis essay — from understanding the rhetorical situation to developing a clear thesis and supporting your claims with evidence. Whether you’re a student tackling this assignment for the first time or looking to refine your academic writing skills, this article will equip you with the strategies needed to write with confidence and clarity.
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is a type of academic writing that explores how an author or speaker uses various techniques to persuade, inform, or inspire an audience. Unlike a summary that simply retells the content, a rhetorical analysis focuses on how the message is delivered and why it is effective.
When writing a rhetorical analysis essay, you examine the purpose of the text, the intended audience, and the strategies the author uses to communicate their ideas. These strategies often include elements such as tone, style, word choice, and the use of rhetorical appeals—ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic).
For example, in Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech, King effectively combines ethos, pathos, and logos to inspire his audience toward unity and justice. His emotional language stirs empathy, his credibility as a civil rights leader strengthens his authority, and his logical arguments for equality make his message compelling and timeless.
Ultimately, a rhetorical analysis essay challenges students to look beyond what is said and understand the deeper methods of persuasion that make a piece of communication powerful and memorable.
Mastering the Rhetorical Triangle and Key Steps in Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
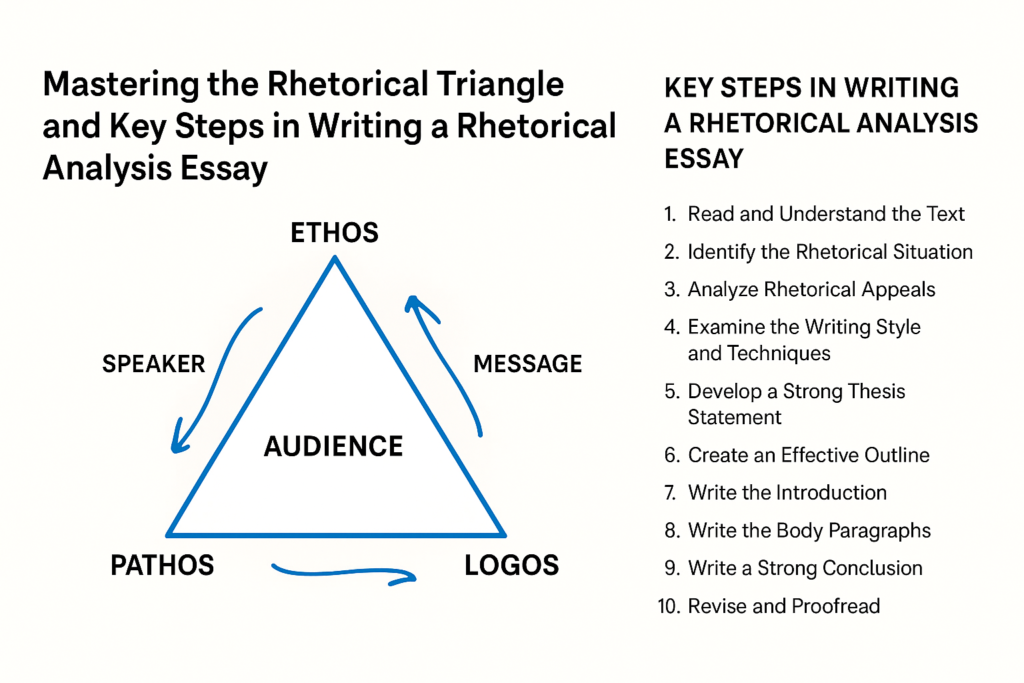
Understanding the Rhetorical Triangle
The rhetorical triangle is a concept developed by the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle to explain how persuasion works. Every effective argument or persuasive text involves three core components — ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic). These elements interact to shape the audience’s response and determine how successfully the message achieves its purpose.
1. Ethos (Credibility)
Ethos refers to the author’s credibility, reliability, and authority. It answers the question:
Can the audience trust the speaker or writer?
A writer establishes ethos by demonstrating expertise, using a professional tone, and showing fairness or integrity. For instance, a scientist citing peer-reviewed research to support an argument about climate change builds ethos because they are qualified to speak on the topic.
In a rhetorical analysis essay, you would identify moments where the author reinforces their credibility. Pay attention to credentials, tone, word choice, and references that position the author as a trustworthy figure.
2. Pathos (Emotion)
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions — compassion, anger, hope, or fear — to make the message more compelling. Emotional appeal can be created through storytelling, vivid imagery, or emotionally charged language.
Example: An advertisement showing heartbreaking images of neglected animals taps into viewers’ empathy and compels them to donate.
In your rhetorical analysis essay, you’ll explore how the author stirs emotion to connect with the audience. Do they use personal anecdotes, strong imagery, or emotive language? Identifying these strategies helps reveal how emotional engagement strengthens persuasion.
3. Logos (Logic)
Logos relies on logic, evidence, and reasoning to appeal to the audience’s intellect. It answers the question:
Does the argument make sense logically?
Authors use facts, statistics, expert opinions, or cause-and-effect reasoning to build logical credibility. For example, a political article that cites verified data to support its claims demonstrates logos.
When writing your rhetorical analysis essay, highlight examples of logical structure and evidence that make the argument convincing. Notice how the author uses data or reasoning to support claims or counter opposing views.
Balancing the Three Appeals

Step 1: Read and Understand the Text
The first step in writing a great rhetorical analysis essay is careful reading and comprehension. Before analyzing, you must fully understand what the author is saying and how they are saying it.
✅ Tips for Effective Reading
- Read twice: The first time, focus on understanding the main message. The second time, focus on rhetorical techniques and tone.
- Highlight key elements: Look for metaphors, repetition, analogies, or emotional language.
- Identify the author’s purpose: Why did they write or deliver this text?
- Notice tone and style: Is it formal, passionate, sarcastic, or calm?
Ask yourself the following guiding questions:
- Who is the author, and what authority do they have?
- What message are they trying to communicate?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What emotions or reactions do they want to evoke?
This active reading strategy will prepare you for a detailed and thoughtful analysis.
Step 2: Identify the Rhetorical Situation
Every rhetorical analysis essay must consider the rhetorical situation, which is the broader context surrounding the text. The rhetorical situation explains why the message exists and how it functions within a specific environment.
Key Elements of the Rhetorical Situation
- Speaker: Who is the author or speaker, and what makes them credible?
- Audience: Who is the message intended for?
- Purpose: What does the author want the audience to think, feel, or do?
- Context: What historical, cultural, or social circumstances influence the text?
- Message: What central argument or theme is being communicated?
Example:
If you’re analyzing Greta Thunberg’s UN Climate Speech, the rhetorical situation includes:
- Speaker: Greta Thunberg, a young environmental activist.
- Audience: Global political leaders and concerned citizens.
- Purpose: To inspire urgent climate action.
- Context: Rising concerns about global warming and political inaction.
- Message: The world’s leaders are not doing enough to protect the planet.
Understanding this situation allows you to interpret the text more accurately and assess how rhetorical strategies fit within its context.
Step 3: Analyze Rhetorical Appeals
Now that you know the context, examine how the author uses ethos, pathos, and logos in practice.
- Ethos (Credibility): Look for signs of authority — professional tone, credentials, or personal experience.
- Pathos (Emotion): Identify emotional language, vivid imagery, or stories that create empathy or anger.
- Logos (Logic): Examine how the author uses reasoning, evidence, and structure to build a persuasive case.
Example:
In Barack Obama’s speeches, all three appeals appear frequently:
- Ethos: He references his role as president and moral duty to lead.
- Pathos: He shares personal stories of American families to inspire unity.
- Logos: He uses economic statistics and logical reasoning to justify policies.
When analyzing, explain how each appeal contributes to the author’s goal and the audience’s response.
Step 4: Examine the Writing Style and Techniques
Beyond rhetorical appeals, a rhetorical analysis essay should discuss the author’s style and delivery — the techniques that shape how the message sounds and feels.
Look for:
- Tone: Is the tone serious, hopeful, or sarcastic?
- Diction: What kind of words are used — formal, simple, or figurative?
- Syntax: How are sentences structured to emphasize key ideas?
- Imagery: What visual or sensory details make the message vivid?
- Repetition and parallelism: Are certain phrases repeated to strengthen a point?
- Figurative language: How do metaphors, analogies, or similes enhance meaning?
Pro Tip: Don’t just identify these elements — explain why they are effective.
Example:
The author’s repetition of “We shall fight” in Winston Churchill’s speech reinforces determination and unity, inspiring the audience through emotional rhythm and strength.
Step 5: Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
A clear thesis statement is the backbone of your rhetorical analysis essay. It summarizes the author’s main strategies and their effect on the audience.
Your thesis should include:
- The author’s purpose.
- The rhetorical techniques used.
- The overall impact or outcome.
Example Thesis:
In her TED Talk, Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie uses storytelling (pathos), credibility (ethos), and logical reasoning (logos) to challenge stereotypes about Africa and promote cultural understanding.
Your thesis guides the entire essay and keeps your analysis focused.
Step 6: Create a Detailed Outline
A well-organized outline helps your rhetorical analysis essay flow logically.
Suggested Structure:
- Introduction: Present the text, context, and thesis.
- Body Paragraph 1 – Ethos: Analyze credibility-building techniques.
- Body Paragraph 2 – Pathos: Explore emotional appeals.
- Body Paragraph 3 – Logos: Examine logic and reasoning.
- Body Paragraph 4 – Style (optional): Discuss tone, diction, and imagery.
- Conclusion: Summarize findings and comment on the text’s effectiveness.
Having a solid outline ensures that your analysis remains organized and comprehensive.
Step 7: Write the Essay
When writing your rhetorical analysis essay, your introduction should immediately grab the reader’s attention and provide necessary context.
Example Introduction:
In his powerful 1963 speech “I Have a Dream,” Martin Luther King Jr. calls for racial equality and civil rights. Through emotional appeals, credible authority, and logical reasoning, King inspires his audience to envision a united and just America.
Each body paragraph should analyze one rhetorical strategy in detail, providing examples and explaining their effectiveness.
Example (Pathos Paragraph):
King’s use of emotional language evokes empathy and urgency. Phrases like “the fierce urgency of now” appeal to his audience’s sense of justice and responsibility. His references to children and future generations create a moral obligation to act, stirring deep emotional commitment among listeners.
Finish with a strong conclusion that summarizes your analysis and highlights the text’s lasting impact.
Example Conclusion:
Through a masterful balance of ethos, pathos, and logos, Martin Luther King Jr. transforms his vision into a timeless call for justice. His rhetorical brilliance continues to inspire movements for equality around the world.
Step 8: Revise and Proofread Carefully
A successful rhetorical analysis essay isn’t just insightful — it’s also polished and professional.
Before submitting:
- Check clarity: Ensure each paragraph connects logically.
- Fix grammar and mechanics: Review spelling, punctuation, and transitions.
- Maintain academic tone: Avoid slang or overly casual language.
- Cite properly: Follow MLA or APA guidelines for quotations.
Pro Tip: Reading your essay aloud helps catch awkward phrasing and ensures a natural flow.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
❌ Summarizing instead of analyzing.
❌ Ignoring the author’s purpose or audience.
❌ Overusing quotes without explanation.
❌ Forgetting to include a clear thesis.
❌ Neglecting proofreading.
Final Thoughts
By following this guide, analyzing rhetorical appeals, and structuring your essay logically, you’ll be able to craft an insightful and high-scoring rhetorical analysis essay.
And if you ever need professional writing help, WriteMastersPro.com is here to support you — from brainstorming topics to editing your final draft.
Expert paper writers are just a few clicks away
Place an order in 3 easy steps. Takes less than 5 mins.